Kit Glossary#
- Channel#
Channel (more precisely called C-Channel) is aluminum that is in the profile of a C. (It is also sometimes called U-Channel.) Channel, along with extrusion, is the most common structural build element in FTC®, and is found in Tetrix, REV, Actobotics, and goBILDA kits.
Channel is fixed pitch, which means that there are pre-drilled holes that limit mounting to finite locations. It can be used to easily construct drivetrains; however, be aware that gear and chain mesh may not be with channel.

- Extrusion#
Extrusion is aluminum shaped into slotted profiles able to accept certain types of hardware. For FTC, the most common is the 15mm extrusion, used in the REV and Misumi products. 15mm extrusion accepts M3 bolts and nuts (note that only regular M3 nuts can fit inside the slot, not locknuts).
Extrusion is not a fixed pitch system, allowing teams to adjust components as they wish. This makes it simple to achieve correct tension and put mechanisms where channel would limit mounting. The adjustability of extrusion is especially useful in precise situations, such as intake geometry. However, extra care must be taken to ensure components do not shift under load.

- Ball Bearing#
Ball bearings refer to bearings with steel balls arranged in a circular fashion. This allows rotation of an element with less friction than a bushing, primarily because the surface area (or contact area) is much less than in a bushing.
Bearings are definitely recommended for drivetrain and high speed usage. Bearings are used in the Actobotics, goBILDA, and REV kits, and are commonly sold by most robotics vendors.

Actobotics dual ball bearing hub#
- Servoblocks#
Servoblocks, sold by Servocity/Actobotics/goBILDA, are a way to mount servos to the goBILDA and Actobotics systems. It is by far the best way to mount servos because it decreases the load on the servo spline, which is the weakest part of the servo. This is because under load, the servo spline teeth can easily become stripped, rendering the servo unusable. While Servoblocks are not cheap, they are one of the best investments for teams to pursue.

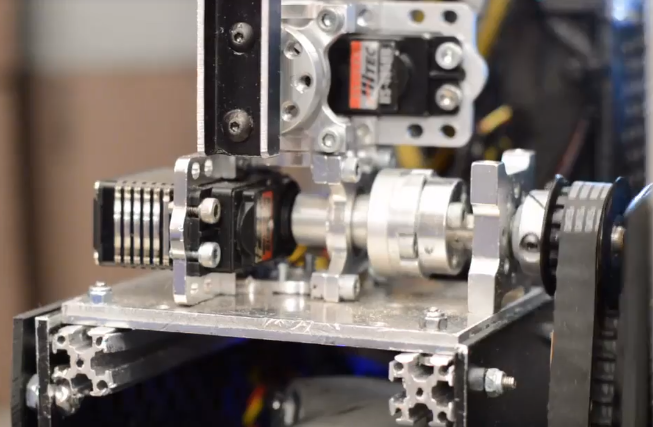
10030 7 Sigma, Relic Recovery#
- Clamping Hub#
A clamping hub is used to fixate part such as sprockets or gears on shafts. It is also used to prevent shafts from moving laterally. Unlike shaft collars, clamping hubs use screws to apply clamping force around the entire shaft, giving a better hold. As a result, clamping hubs are recommended over shaft collars.

- Bevel gear#
Bevel gears are gears that transfer power along different axes, which are perpendicular to each other. Bevel gears are generally considered more inefficient than regular gears.
However, bevel gears can be very useful, especially in areas of limited space where the motor can be placed perpendicular to the element it is driving, and not in the same plane.
3736 Serious Business, Rover Ruckus#
- Lead Screw#
A lead screw is very similar to a threaded rod. It is used for high load and high torque application such as hanging. However, due to the nature of the threaded rod, lead screws are generally quite slow compared to linear slides. The speed of a lead screw is determined by two factors. The first is how fast the motor outputs, and the second is the number of threads per inch (TPI).

- Shaft#
A shaft is a piece of shaped metal used in power transmission. Shafts are the primary method to transfer power from motor to wheel. Generally, shafts are made out of steel, so do not use a bandsaw to cut a shaft. Rather, use a hacksaw, as hacksaw blades can cut through steel. There are different kinds of bores in FTC, which are listed below.
Round shaft
D-shaft: has a flat part for set screws, otherwise round
Hex shaft: six sided shaft
Rounded Hex shaft: hex shaft that’s been rounded so that it can run in round bearings
Keyed shaft: round shaft which has a keyway (a slot) through the shaft
- Locknut#
A locknut is a nut that resists vibration by the nyloc inside. Nyloc is a type of plastic that holds the bolt securely on to the nut when it is screwed in. It is advised that teams purchase locknuts instead of regular nuts as FTC mechanisms often become loose over time.
- Bushing#
A bushing is primarily mounted on the outside of a shaft. It rotates in a pillow block, which holds the bushing. Generally, both are made out of a low-friction material such as Delrin or bronze.
Bushings are less efficient than ball bearings because they have a larger surface of contact, but are acceptable for low-load situations or low-budget teams.
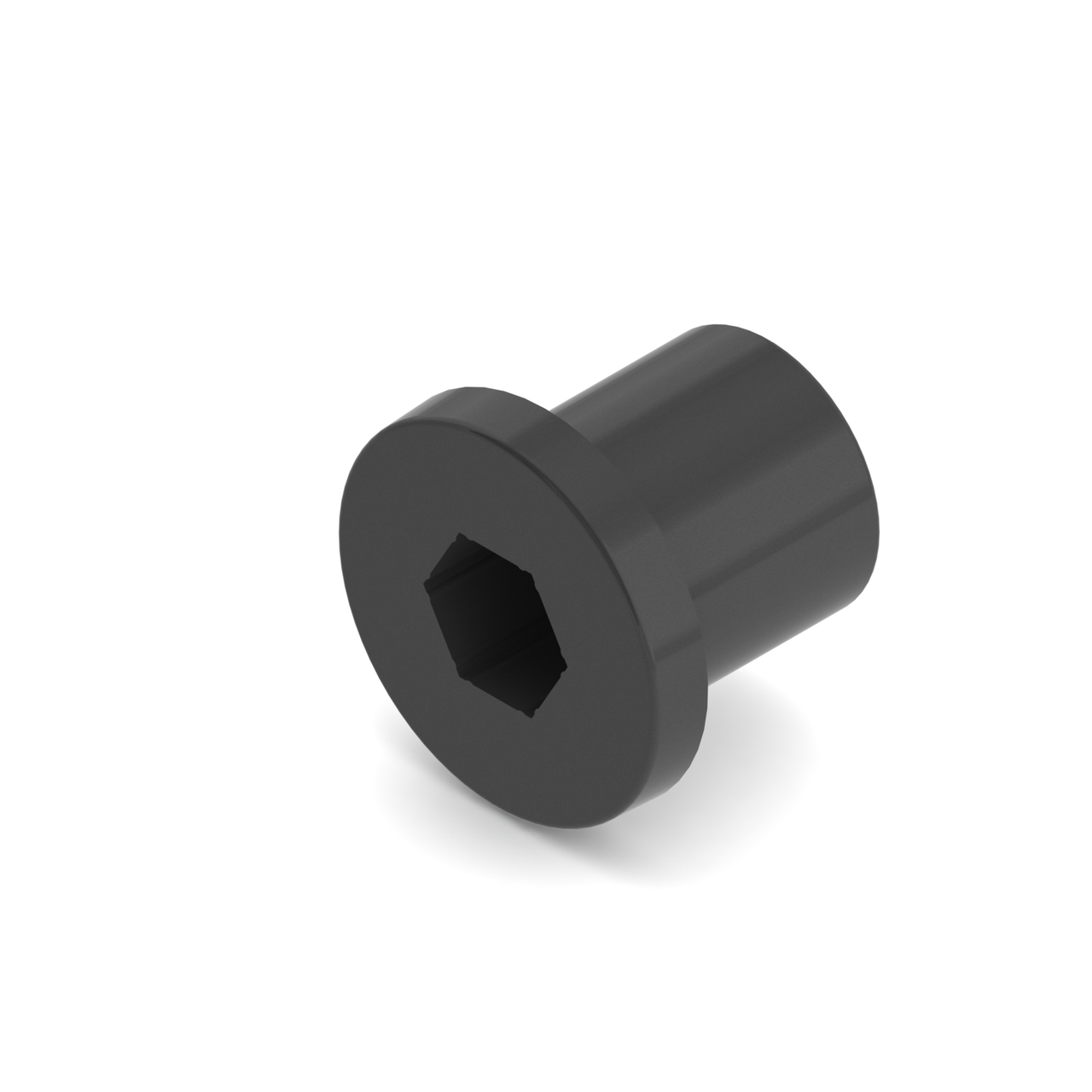

REV Bushing#
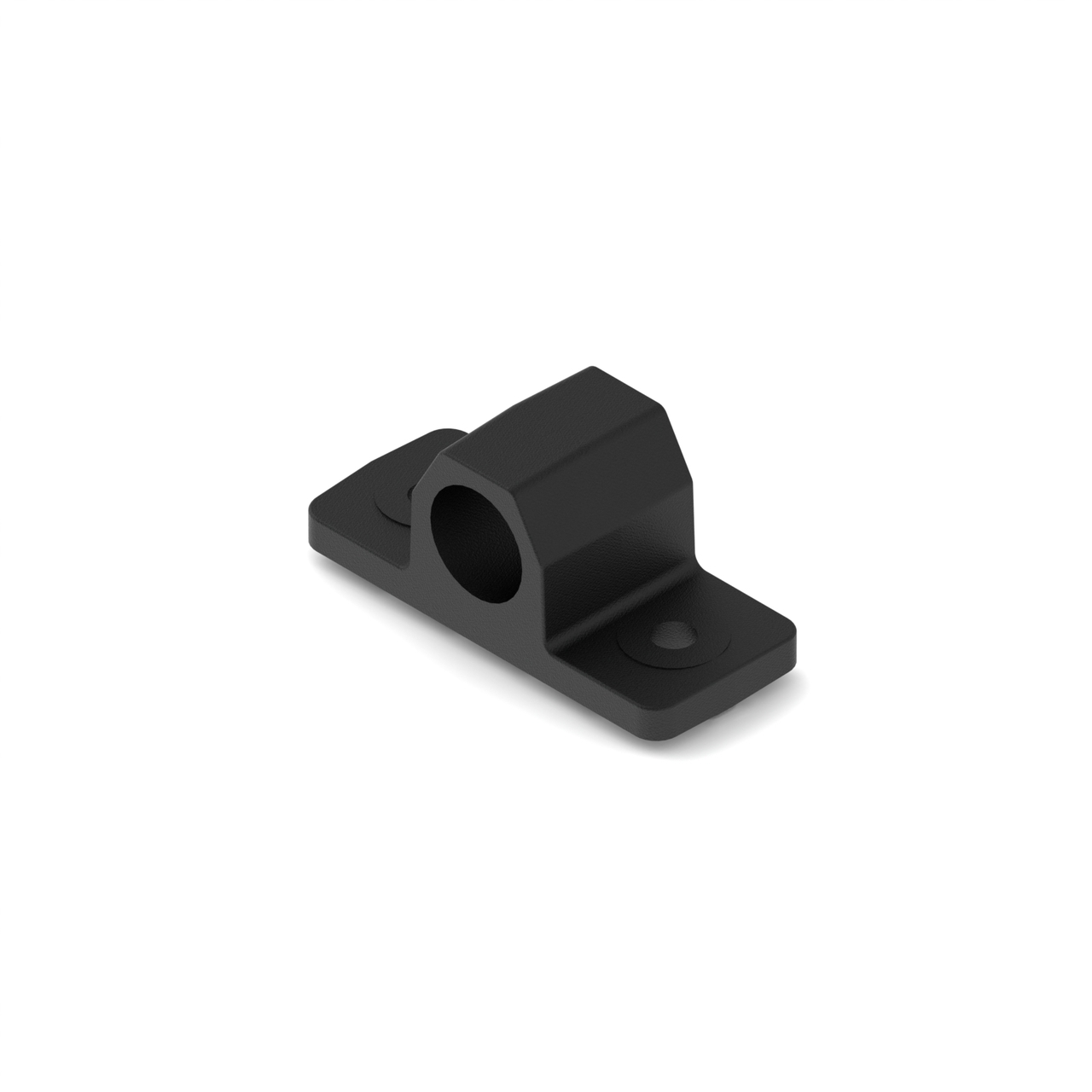

REV Pillow Block#
- Churro#
Churro is a 1/2” or 3/8” hex product sold by AndyMark. It has a bore that is easily tapped to accommodate 1/4-20 and 1/4-28 bolts, and is commonly used as a large standoff. It is light and cheap compared to other hex products.
Warning
Using churro as shaft is highly discouraged, as it is slightly undersized as well as prone to twisting.
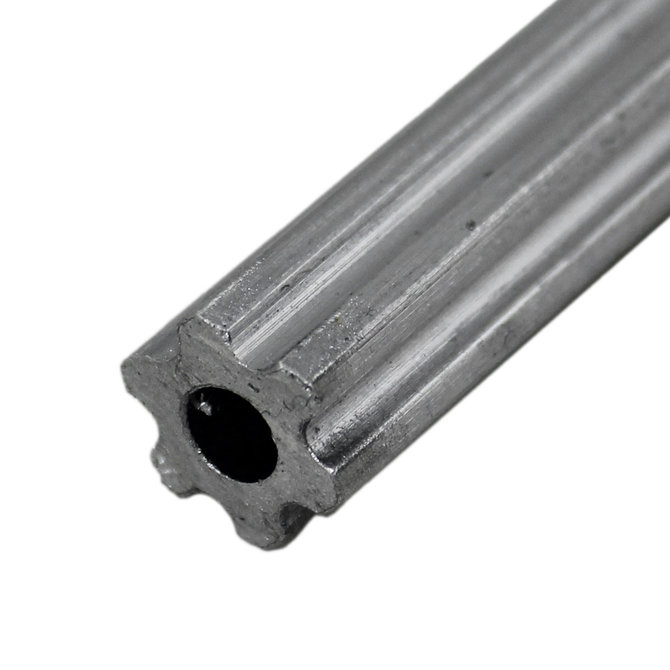

- Set Screw#
A set screw is generally a hex socket screw that is used to fasten parts such as sprockets or gears to a shaft, or to fix a shaft in place so that it doesn’t move around. Due to the hex socket, allen keys must be used to tighten and loosen set screws.
Warning
Set screws are not recommended for drivetrain and high-load applications since there is very little surface area in contact with the shaft (only the tip of the screw). This makes the set screw likely to damage the shaft. Therefore, set screws can become loose very easily.
If set screws must be used, then it is imperative to use Loctite to reduce the chance of them shaking loose.
Note
Clamping hubs are much preferred to set screws, as clamping hubs apply pressure to the whole diameter of the shaft, as opposed to just one point.

- Shaft Collar#
A shaft collar, which has a set screw, is fitted on to a shaft in order to secure parts.

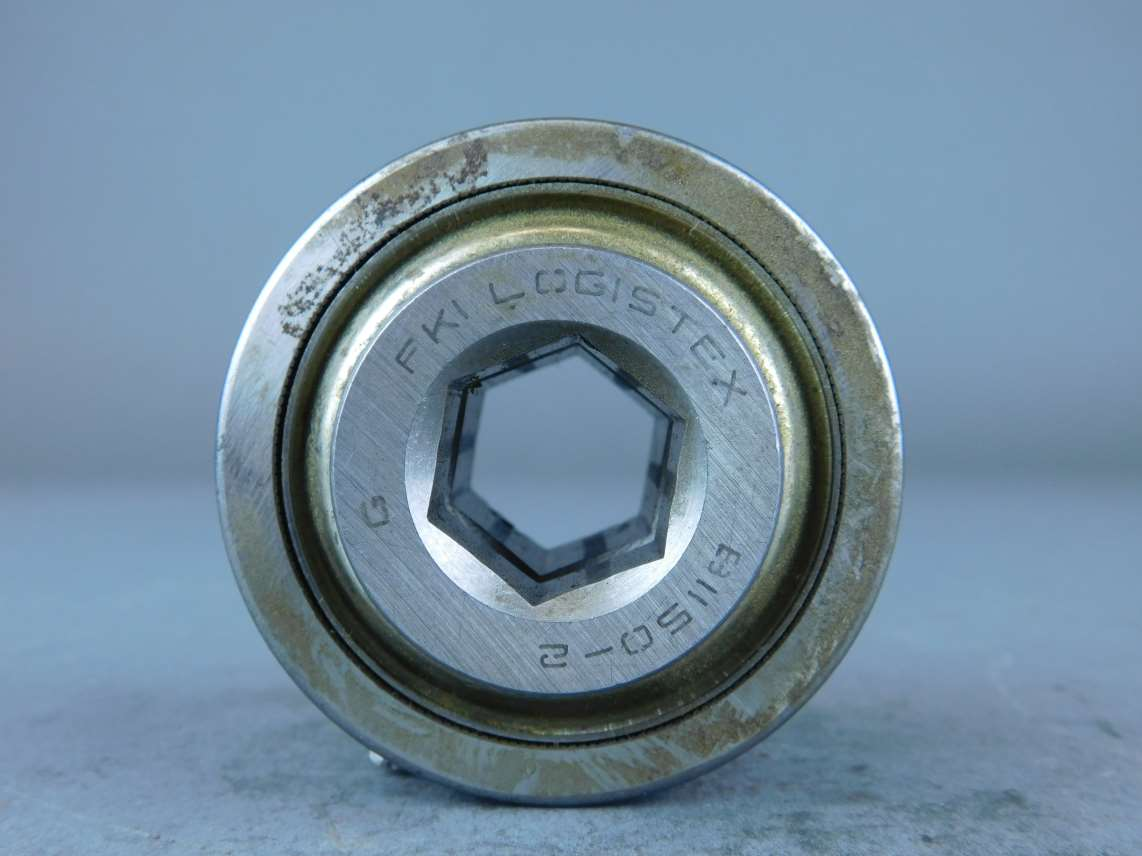
- Bore#
The bore refers to the shape of the opening that the shaft is inserted into. For example, the bore for a 5 mm hex shaft is the hexagonal shape.
“Stripping the bore” means that over time, the bore will lose its hexagonal shape, and become close to a circular shape, rendering the bore (and subsequently, the part it is on) useless.

- Clamp Mounting#
Clamp mounting refers to securing a motor primarily by using friction instead of screws attached to the motor itself. This is generally discouraged as the motor can become loosened over time.
Tip
Use friction tape around the surface of the motor that is clamped down so that it will have less chance of moving around.
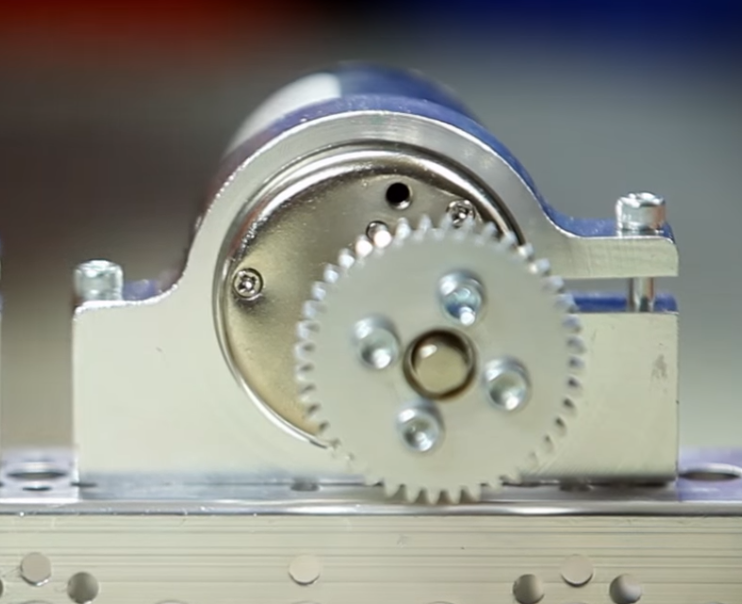
TETRIX clamp mount and v1 motor#
- Face Mounting#
Face mounting refers to mounting the motor by affixing the motor directly to the mount using bolts. This is the preferable way of mounting the motor (compared to clamp mounting) because it is less likely to loosen over time, especially with the use of Loctite on the bolts.
Note
It is advisable that 4-6 bolts be used to face mount for redundancy.
Additionally, there is no way that the motor might rotate and cause a loss of tension in belts or chain.
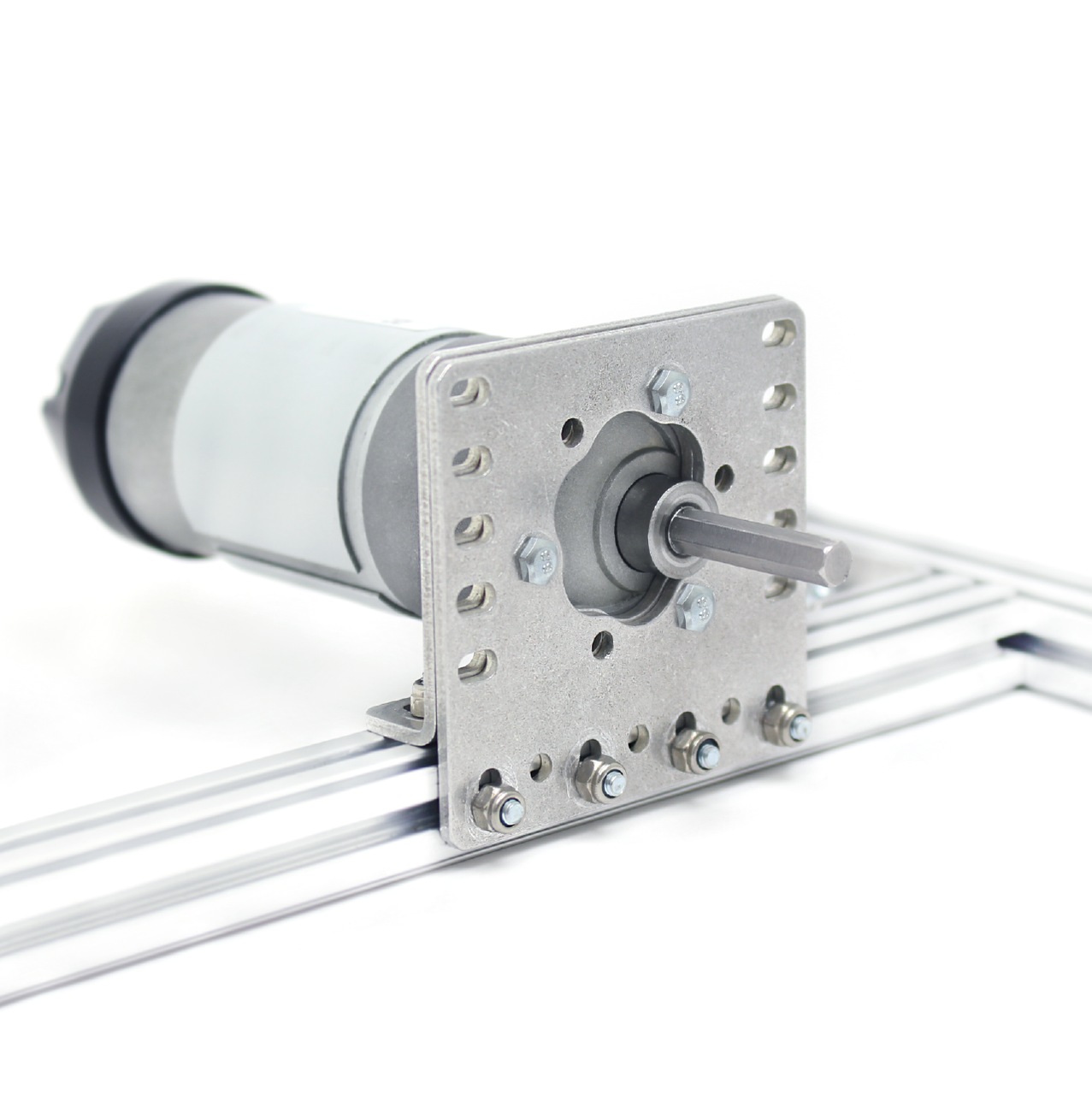

REV v2 Motor Facemounted#