Passive Intake/Claw#
Passive intakes are mechanisms in which the driver must pick up individual items, usually by actuating some sort of gripper, which holds the game element.
Claws are the most common sort of passive intake and probably one of the first mechanisms that jump to mind during brainstorming. Unlike most intakes, claws can be made with only servos, and thus don’t require valuable motor slots.
This is not to say there are no disadvantages; notably, unlike intakes, when you pick up something with a claw, it isn’t easy to transfer the collected element to a separate scoring mechanism. For this reason, in most cases, claws double as both a collection method and a scoring method.
Claws are extremely useful for picking up large, unwieldy elements that cannot be controlled by active intakes. For example, the relic in Relic Recovery would be much harder to control using a more active intake; so teams used a claw.
Attention
However, claws are outclassed by active intakes for picking up small game pieces in nearly every game.
Advantages#
Much simpler than an intake
Takes a lot less time to build than a reliable intake + transfer
Less moving parts = less things that can go wrong
Usually does not take up a motor slot
Can pick up odd shaped game elements that active intakes can’t
Disadvantages#
Depending on their use case, claws are slower than intakes.
The driver must angle the robot, position the claw, and grab the game element.
By contrast, with an intake, the driver needs only to position the intake and grab the game elements.
Claws can be more fragile and break easily.
In cases in which claws are slower than intakes, they can be much more prone to defensive maneuvers. The more time spent collecting, the more vulnerable you are.

11115 Gluten Free, Finalist Alliance Captain (Detroit), Relic Recovery#

8680 Kraken-Pinion, Relic Recovery#
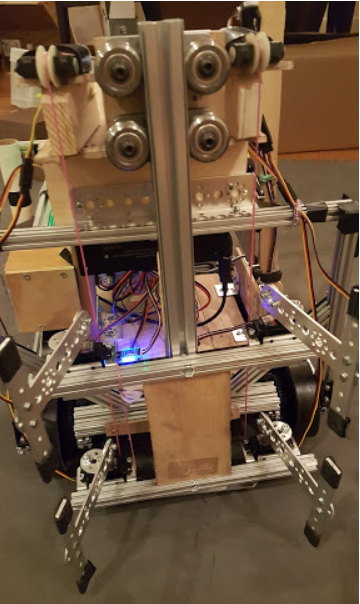
13075 Coram Deo Academy Robotics, Relic Recovery (suboptimal use case)#